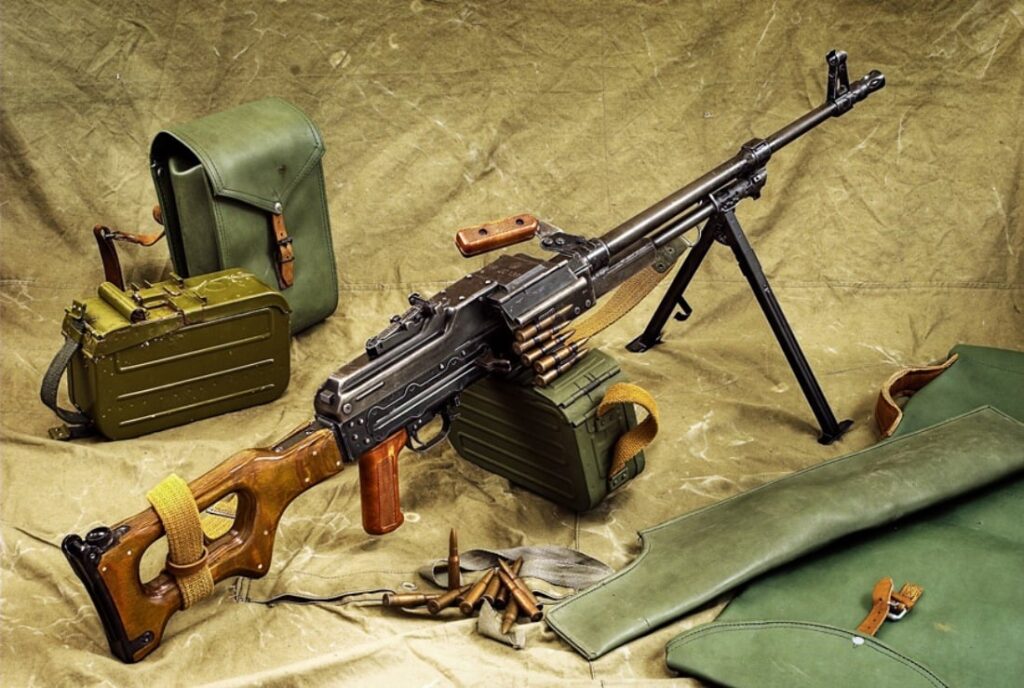
The PKM(Kalashnikov Machine Gun) is a light machine gun of Soviet origin designed by Mikhail Kalashnikov. Introduced in 1969 as an improvement on the PMK, it rapidly became one of the most widely used light machine guns in the world. Its robustness, reliability and ease of maintenance make it the weapon of choice for many countries and armed groups.
History of PKM
The PKM was introduced to replace the RPD, which had become obsolete in the context of new military doctrines. Designed for use by a two-person team, the PKM is lightweight yet capable of sustained firepower.
It uses the same 7.62×54 mm cartridge as the SVD Dragunov rifle, ensuring simplified logistics in the field. Since its introduction, it has been adopted in over 80 countries and is still in production, with several modern variants.
Technical data
Caliber: 7.62×54 mm
Weight: Approx. 7.5 kg without ammunition
Total length: 1,160 mm
Barrel length: 658 mm
Magazine capacity: 100 or 200 cartridge belt
Firing rate: 650 to 750 shots per minute
Effective range: 1,000 m
Mechanism: Gas borrowing operation
Materials: Steel and polymers for weight reduction
Advantages of PKM
The PKM is distinguished by a number of features that make it particularly effective on the battlefield:
Legendary reliability: Designed to operate in extreme conditions (sand, mud, snow), it can pull without intensive maintenance.
Lightweight: Compared to other machine guns in its class, it’s relatively easy to carry.
Easy maintenance: its components are easy to dismantle and clean.
Versatility: it can be mounted on a tripod, used by a sniper or installed on vehicles.
Comparison with other machine guns
| Model | Caliber | Weight (kg) | Rate of fire (cpm) | Effective range (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKM | 7.62×54 mm | 7,5 | 650-750 | 1 000 |
| M240 | 7.62×51 mm | 12,5 | 650-950 | 1 800 |
| FN Minimi | 5.56×45 mm | 7,1 | 700-1 150 | 800 |
| RPK | 7.62×39 mm | 5 | 600-660 | 800 |
The PKM stands out for its balance between firepower and maneuverability. Although heavier than the RPK, it offers superior range and rate of fire. Compared with the M240, it is much lighter, making it a more practical option for operations on foot.
Contemporary use
Today, the PKM remains a global benchmark for light machine guns. Its modernized variants incorporate rails for accessories (optics, laser pointers), improved barrels for extended service life, and even lighter materials to meet today’s military requirements.
Its low production cost and durability make it a preferred choice in countries with limited resources.